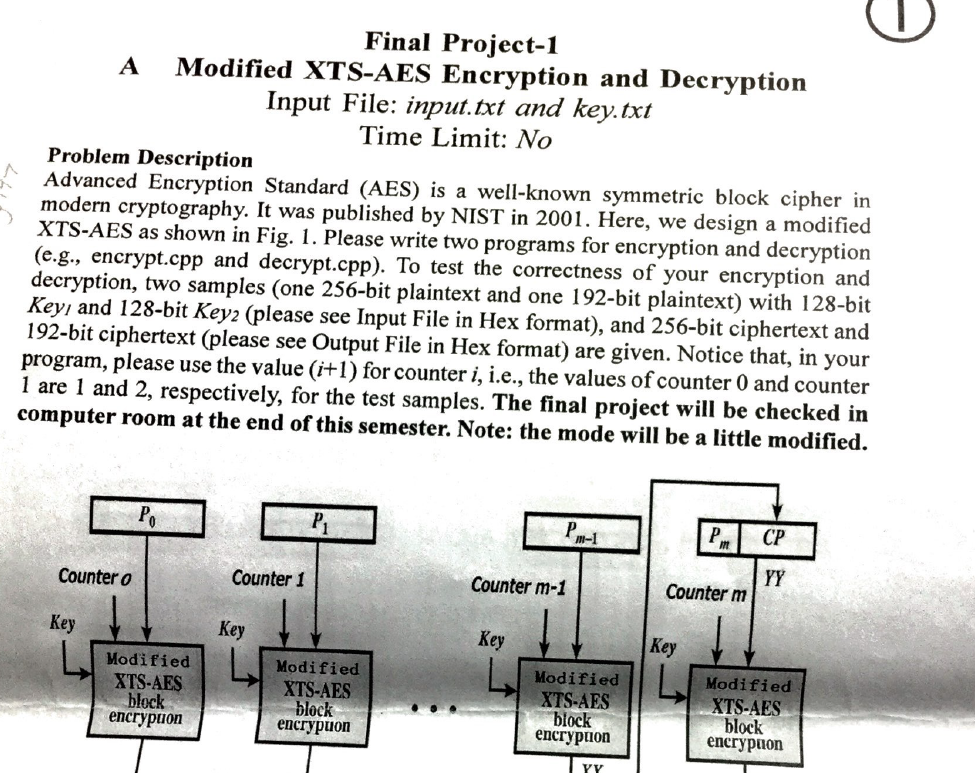
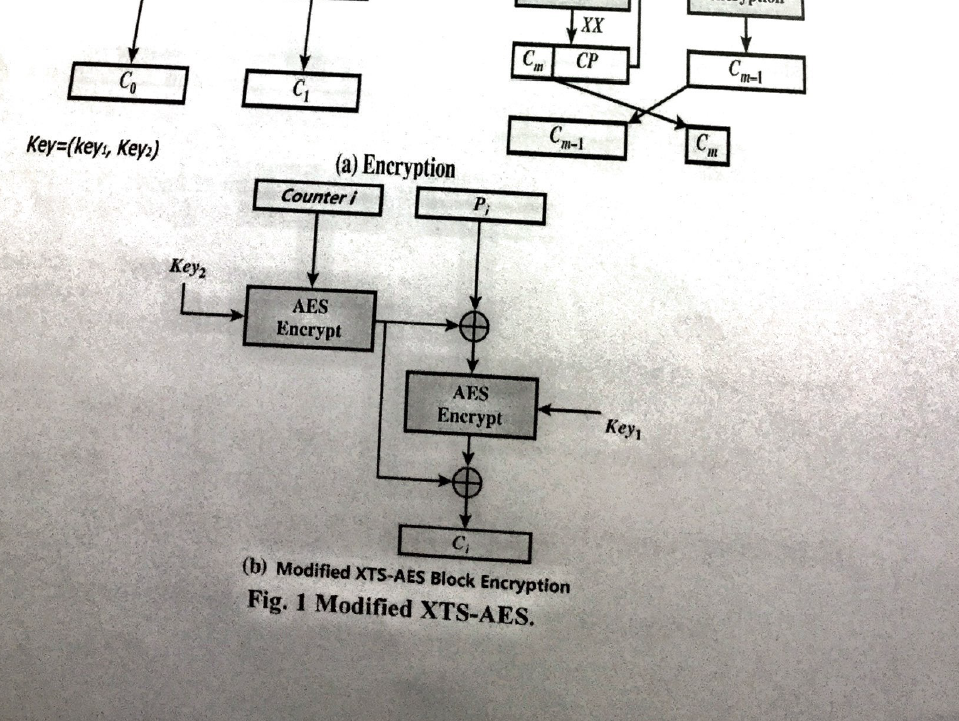


Final Project-1 A Modified XTS-AES Encryption and Decryption Input File: input. and key txt Time Limit: No Problem Description Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a well-known symmetric block cipher in modern cryptography. It was published by NIST in 2001. Here, we design a modified XTS-AES as shown in Fig. 1. Please write two programs for encryption and decryption (e.g., encrypt.cpp and decrypt.cpp). To test the correctness of your encryption and decryption, two samples (one 256-bit plaintext and one 192-bit plaintext with 128-bit Keyn and 128-bit Key2 (please see Input File in Hex format), and 256-bit ciphertext and 192-bit ciphertext please see Output File in Hex format) are given. Notice that, in your program, please use the value (it1) for counter i, i.e., the values ofcounter 0 and counter l are 1 and 2, respectively, for the test samples. The final project will be checked in computer room at the end of this semester. Note: the mode will be a little modified. P CP Counter 0 Counter 1 Counter m-1 Counter m Key Key Key Key Modified Modified Modified XTS-AES Modified XTS-AES XTS-AES block XTS-AES block block encrypuon block encryption encryption encrypilon YY
Expert Answer
*/
// Include stdio.h for standard input/output.
// Used for giving output to the screen.
#include<stdio.h>
// The number of columns comprising a state in AES. This is a constant in AES. Value=4
#define Nb 4
// The number of rounds in AES Cipher. It is simply initiated to zero. The actual value is recieved in the program.
int Nr=0;
// The number of 32 bit words in the key. It is simply initiated to zero. The actual value is recieved in the program.
int Nk=0;
// in – it is the array that holds the plain text to be encrypted.
// out – it is the array that holds the key for encryption.
// state – the array that holds the intermediate results during encryption.
unsigned char in[16], out[16], state[4][4];
// The array that stores the round keys.
unsigned char RoundKey[240];
// The Key input to the AES Program
unsigned char Key[32];
int getSBoxValue(int num)
{
//giving input in program itself. if input to be read from file input.txt , key.txt then comment the below part and in main() function reading file file code to be executed.
int sbox[256] = {
//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
0x63, 0x7c, 0x77, 0x7b, 0xf2, 0x6b, 0x6f, 0xc5, 0x30, 0x01, 0x67, 0x2b, 0xfe, 0xd7, 0xab, 0x76, //0
0xca, 0x82, 0xc9, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0x59, 0x47, 0xf0, 0xad, 0xd4, 0xa2, 0xaf, 0x9c, 0xa4, 0x72, 0xc0, //1
0xb7, 0xfd, 0x93, 0x26, 0x36, 0x3f, 0xf7, 0xcc, 0x34, 0xa5, 0xe5, 0xf1, 0x71, 0xd8, 0x31, 0x15, //2
0x04, 0xc7, 0x23, 0xc3, 0x18, 0x96, 0x05, 0x9a, 0x07, 0x12, 0x80, 0xe2, 0xeb, 0x27, 0xb2, 0x75, //3
0x09, 0x83, 0x2c, 0x1a, 0x1b, 0x6e, 0x5a, 0xa0, 0x52, 0x3b, 0xd6, 0xb3, 0x29, 0xe3, 0x2f, 0x84, //4
0x53, 0xd1, 0x00, 0xed, 0x20, 0xfc, 0xb1, 0x5b, 0x6a, 0xcb, 0xbe, 0x39, 0x4a, 0x4c, 0x58, 0xcf, //5
0xd0, 0xef, 0xaa, 0xfb, 0x43, 0x4d, 0x33, 0x85, 0x45, 0xf9, 0x02, 0x7f, 0x50, 0x3c, 0x9f, 0xa8, //6
0x51, 0xa3, 0x40, 0x8f, 0x92, 0x9d, 0x38, 0xf5, 0xbc, 0xb6, 0xda, 0x21, 0x10, 0xff, 0xf3, 0xd2, //7
0xcd, 0x0c, 0x13, 0xec, 0x5f, 0x97, 0x44, 0x17, 0xc4, 0xa7, 0x7e, 0x3d, 0x64, 0x5d, 0x19, 0x73, //8
0x60, 0x81, 0x4f, 0xdc, 0x22, 0x2a, 0x90, 0x88, 0x46, 0xee, 0xb8, 0x14, 0xde, 0x5e, 0x0b, 0xdb, //9
0xe0, 0x32, 0x3a, 0x0a, 0x49, 0x06, 0x24, 0x5c, 0xc2, 0xd3, 0xac, 0x62, 0x91, 0x95, 0xe4, 0x79, //A
0xe7, 0xc8, 0x37, 0x6d, 0x8d, 0xd5, 0x4e, 0xa9, 0x6c, 0x56, 0xf4, 0xea, 0x65, 0x7a, 0xae, 0x08, //B
0xba, 0x78, 0x25, 0x2e, 0x1c, 0xa6, 0xb4, 0xc6, 0xe8, 0xdd, 0x74, 0x1f, 0x4b, 0xbd, 0x8b, 0x8a, //C
0x70, 0x3e, 0xb5, 0x66, 0x48, 0x03, 0xf6, 0x0e, 0x61, 0x35, 0x57, 0xb9, 0x86, 0xc1, 0x1d, 0x9e, //D
0xe1, 0xf8, 0x98, 0x11, 0x69, 0xd9, 0x8e, 0x94, 0x9b, 0x1e, 0x87, 0xe9, 0xce, 0x55, 0x28, 0xdf, //E
0x8c, 0xa1, 0x89, 0x0d, 0xbf, 0xe6, 0x42, 0x68, 0x41, 0x99, 0x2d, 0x0f, 0xb0, 0x54, 0xbb, 0x16 }; //F
return sbox[num];
}
// The round constant word array, Rcon[i], contains the values given by
// x to th e power (i-1) being powers of x (x is denoted as {02}) in the field GF(28)
// Note that i starts at 1, not 0).
int Rcon[255] = {
0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a,
0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63, 0xc6, 0x97, 0x35, 0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef, 0xc5, 0x91, 0x39,
0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd, 0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f, 0x25, 0x4a, 0x94, 0x33, 0x66, 0xcc, 0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a,
0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb, 0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8,
0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a, 0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63, 0xc6, 0x97, 0x35, 0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef,
0xc5, 0x91, 0x39, 0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd, 0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f, 0x25, 0x4a, 0x94, 0x33, 0x66, 0xcc,
0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a, 0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb, 0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b,
0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a, 0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63, 0xc6, 0x97, 0x35, 0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3,
0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef, 0xc5, 0x91, 0x39, 0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd, 0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f, 0x25, 0x4a, 0x94,
0x33, 0x66, 0xcc, 0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a, 0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb, 0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20,
0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a, 0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63, 0xc6, 0x97, 0x35,
0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef, 0xc5, 0x91, 0x39, 0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd, 0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f,
0x25, 0x4a, 0x94, 0x33, 0x66, 0xcc, 0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a, 0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb, 0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04,
0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a, 0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63,
0xc6, 0x97, 0x35, 0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef, 0xc5, 0x91, 0x39, 0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd,
0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f, 0x25, 0x4a, 0x94, 0x33, 0x66, 0xcc, 0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a, 0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb };
// This function produces Nb(Nr+1) round keys. The round keys are used in each round to encrypt the states.
void KeyExpansion()
{
int i,j;
unsigned char temp[4],k;
// The first round key is the key itself.
for(i=0;i<Nk;i++)
{
RoundKey[i*4]=Key[i*4];
RoundKey[i*4+1]=Key[i*4+1];
RoundKey[i*4+2]=Key[i*4+2];
RoundKey[i*4+3]=Key[i*4+3];
}
// All other round keys are found from the previous round keys.
while (i < (Nb * (Nr+1)))
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
temp[j]=RoundKey[(i-1) * 4 + j];
}
if (i % Nk == 0)
{
// This function rotates the 4 bytes in a word to the left once.
// [a0,a1,a2,a3] becomes [a1,a2,a3,a0]
// Function RotWord()
{
k = temp[0];
temp[0] = temp[1];
temp[1] = temp[2];
temp[2] = temp[3];
temp[3] = k;
}
// SubWord() is a function that takes a four-byte input word and
// applies the S-box to each of the four bytes to produce an output word.
// Function Subword()
{
temp[0]=getSBoxValue(temp[0]);
temp[1]=getSBoxValue(temp[1]);
temp[2]=getSBoxValue(temp[2]);
temp[3]=getSBoxValue(temp[3]);
}
temp[0] = temp[0] ^ Rcon[i/Nk];
}
else if (Nk > 6 && i % Nk == 4)
{
// Function Subword()
{
temp[0]=getSBoxValue(temp[0]);
temp[1]=getSBoxValue(temp[1]);
temp[2]=getSBoxValue(temp[2]);
temp[3]=getSBoxValue(temp[3]);
}
}
RoundKey[i*4+0] = RoundKey[(i-Nk)*4+0] ^ temp[0];
RoundKey[i*4+1] = RoundKey[(i-Nk)*4+1] ^ temp[1];
RoundKey[i*4+2] = RoundKey[(i-Nk)*4+2] ^ temp[2];
RoundKey[i*4+3] = RoundKey[(i-Nk)*4+3] ^ temp[3];
i++;
}
}
// This function adds the round key to state.
// The round key is added to the state by an XOR function.
void AddRoundKey(int round)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
state[j][i] ^= RoundKey[round * Nb * 4 + i * Nb + j];
}
}
}
// The SubBytes Function Substitutes the values in the
// state matrix with values in an S-box.
void SubBytes()
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
state[i][j] = getSBoxValue(state[i][j]);
}
}
}
// The ShiftRows() function shifts the rows in the state to the left.
// Each row is shifted with different offset.
// Offset = Row number. So the first row is not shifted.
void ShiftRows()
{
unsigned char temp;
// Rotate first row 1 columns to left
temp=state[1][0];
state[1][0]=state[1][1];
state[1][1]=state[1][2];
state[1][2]=state[1][3];
state[1][3]=temp;
// Rotate second row 2 columns to left
temp=state[2][0];
state[2][0]=state[2][2];
state[2][2]=temp;
temp=state[2][1];
state[2][1]=state[2][3];
state[2][3]=temp;
// Rotate third row 3 columns to left
temp=state[3][0];
state[3][0]=state[3][3];
state[3][3]=state[3][2];
state[3][2]=state[3][1];
state[3][1]=temp;
}
// xtime is a macro that finds the product of {02} and the argument to xtime modulo {1b}
#define xtime(x) ((x<<1) ^ (((x>>7) & 1) * 0x1b))
// MixColumns function mixes the columns of the state matrix
void MixColumns()
{
int i;
unsigned char Tmp,Tm,t;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
t=state[0][i];
Tmp = state[0][i] ^ state[1][i] ^ state[2][i] ^ state[3][i] ;
Tm = state[0][i] ^ state[1][i] ; Tm = xtime(Tm); state[0][i] ^= Tm ^ Tmp ;
Tm = state[1][i] ^ state[2][i] ; Tm = xtime(Tm); state[1][i] ^= Tm ^ Tmp ;
Tm = state[2][i] ^ state[3][i] ; Tm = xtime(Tm); state[2][i] ^= Tm ^ Tmp ;
Tm = state[3][i] ^ t ; Tm = xtime(Tm); state[3][i] ^= Tm ^ Tmp ;
}
}
// Cipher is the main function that encrypts the PlainText.
void Cipher()
{
int i,j,round=0;
//Copy the input PlainText to state array.
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
state[j][i] = in[i*4 + j];
}
}
// Add the First round key to the state before starting the rounds.
AddRoundKey(0);
// There will be Nr rounds.
// The first Nr-1 rounds are identical.
// These Nr-1 rounds are executed in the loop below.
for(round=1;round<Nr;round++)
{
SubBytes();
ShiftRows();
MixColumns();
AddRoundKey(round);
}
// The last round is given below.
// The MixColumns function is not here in the last round.
SubBytes();
ShiftRows();
AddRoundKey(Nr);
// The encryption process is over.
// Copy the state array to output array.
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
out[i*4+j]=state[j][i];
}
}
}
void main()
{
int i;
// Recieve the length of key here.
while(Nr!=128 && Nr!=192 && Nr!=256)
{
printf(“Enter the length of Key(128, 192 or 256 only): “);
scanf(“%d”,&Nr);
}
// Calculate Nk and Nr from the recieved value.
Nk = Nr / 32;
Nr = Nk + 6;
// The array temp stores the key.
// The array temp2 stores the plaintext.
unsigned char temp[16] = {0x00 ,0x01 ,0x02 ,0x03 ,0x04 ,0x05 ,0x06 ,0x07 ,0x08 ,0x09 ,0x0a ,0x0b ,0x0c ,0x0d ,0x0e ,0x0f};
unsigned char temp2[16]= {0x00 ,0x11 ,0x22 ,0x33 ,0x44 ,0x55 ,0x66 ,0x77 ,0x88 ,0x99 ,0xaa ,0xbb ,0xcc ,0xdd ,0xee ,0xff};
// Copy the Key and PlainText
for(i=0;i<Nk*4;i++)
{
Key[i]=temp[i];
in[i]=temp2[i];
}
// *********************************************************
//Clear the input buffer
flushall();
//Recieve the key from the user
printf(“Enter the Key in hexadecimal: “);
for(i=0;i<Nk*4;i++)
{
scanf(“%x”,&Key[i]);
}
printf(“Enter the PlainText in hexadecimal: “);
for(i=0;i<Nb*4;i++)
{
scanf(“%x”,&in[i]);
}
//to read the plain text and key from text files.(plain,txt,key.txt)
FILE * pt_file;
string str;
pt_file = fopen( "plain.txt" , "r");
if (pt_file) {
while (fscanf(pt_file, "%s", str)!=EOF)
{
for(i=0;i<Nb*4;i++)
{
in[i]=str;
}
}
fclose(pt_file);
FILE * key_file;
key_file = fopen( "key.txt" , "r");
if (key_file) {
while (fscanf(key_file, "%s", str)!=EOF)
{
for(i=0;i<Nk*4;i++)
{
key[i]=str;
}
}
fclose(key_file);
// The KeyExpansion routine must be called before encryption.
KeyExpansion();
// The next function call encrypts the PlainText with the Key using AES algorithm.
Cipher();
// Output the encrypted text.
printf(“nText after encryption:n”);
for(i=0;i<Nk*4;i++)
{
printf(“%02x “,out[i]);
}
printf(“nn”);
}
AES Decryption,
// Include stdio.h for standard input/output.
// Used for giving output to the screen.
#include<stdio.h>
// The number of columns comprising a state in AES. This is a constant in AES. Value=4
#define Nb 4
// The number of rounds in AES Cipher. It is simply initiated to zero. The actual value is recieved in the program.
int Nr=0;
// The number of 32 bit words in the key. It is simply initiated to zero. The actual value is recieved in the program.
int Nk=0;
// in – it is the array that holds the CipherText to be decrypted.
// out – it is the array that holds the output of the for decryption.
// state – the array that holds the intermediate results during decryption.
unsigned char in[16], out[16], state[4][4];
// The array that stores the round keys.
unsigned char RoundKey[240];
// The Key input to the AES Program
unsigned char Key[32];
int getSBoxInvert(int num)
{
int rsbox[256] =
{ 0x52, 0x09, 0x6a, 0xd5, 0x30, 0x36, 0xa5, 0x38, 0xbf, 0x40, 0xa3, 0x9e, 0x81, 0xf3, 0xd7, 0xfb
, 0x7c, 0xe3, 0x39, 0x82, 0x9b, 0x2f, 0xff, 0x87, 0x34, 0x8e, 0x43, 0x44, 0xc4, 0xde, 0xe9, 0xcb
, 0x54, 0x7b, 0x94, 0x32, 0xa6, 0xc2, 0x23, 0x3d, 0xee, 0x4c, 0x95, 0x0b, 0x42, 0xfa, 0xc3, 0x4e
, 0x08, 0x2e, 0xa1, 0x66, 0x28, 0xd9, 0x24, 0xb2, 0x76, 0x5b, 0xa2, 0x49, 0x6d, 0x8b, 0xd1, 0x25
, 0x72, 0xf8, 0xf6, 0x64, 0x86, 0x68, 0x98, 0x16, 0xd4, 0xa4, 0x5c, 0xcc, 0x5d, 0x65, 0xb6, 0x92
, 0x6c, 0x70, 0x48, 0x50, 0xfd, 0xed, 0xb9, 0xda, 0x5e, 0x15, 0x46, 0x57, 0xa7, 0x8d, 0x9d, 0x84
, 0x90, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x00, 0x8c, 0xbc, 0xd3, 0x0a, 0xf7, 0xe4, 0x58, 0x05, 0xb8, 0xb3, 0x45, 0x06
, 0xd0, 0x2c, 0x1e, 0x8f, 0xca, 0x3f, 0x0f, 0x02, 0xc1, 0xaf, 0xbd, 0x03, 0x01, 0x13, 0x8a, 0x6b
, 0x3a, 0x91, 0x11, 0x41, 0x4f, 0x67, 0xdc, 0xea, 0x97, 0xf2, 0xcf, 0xce, 0xf0, 0xb4, 0xe6, 0x73
, 0x96, 0xac, 0x74, 0x22, 0xe7, 0xad, 0x35, 0x85, 0xe2, 0xf9, 0x37, 0xe8, 0x1c, 0x75, 0xdf, 0x6e
, 0x47, 0xf1, 0x1a, 0x71, 0x1d, 0x29, 0xc5, 0x89, 0x6f, 0xb7, 0x62, 0x0e, 0xaa, 0x18, 0xbe, 0x1b
, 0xfc, 0x56, 0x3e, 0x4b, 0xc6, 0xd2, 0x79, 0x20, 0x9a, 0xdb, 0xc0, 0xfe, 0x78, 0xcd, 0x5a, 0xf4
, 0x1f, 0xdd, 0xa8, 0x33, 0x88, 0x07, 0xc7, 0x31, 0xb1, 0x12, 0x10, 0x59, 0x27, 0x80, 0xec, 0x5f
, 0x60, 0x51, 0x7f, 0xa9, 0x19, 0xb5, 0x4a, 0x0d, 0x2d, 0xe5, 0x7a, 0x9f, 0x93, 0xc9, 0x9c, 0xef
, 0xa0, 0xe0, 0x3b, 0x4d, 0xae, 0x2a, 0xf5, 0xb0, 0xc8, 0xeb, 0xbb, 0x3c, 0x83, 0x53, 0x99, 0x61
, 0x17, 0x2b, 0x04, 0x7e, 0xba, 0x77, 0xd6, 0x26, 0xe1, 0x69, 0x14, 0x63, 0x55, 0x21, 0x0c, 0x7d };
return rsbox[num];
}
int getSBoxValue(int num)
{
int sbox[256] = {
//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
0x63, 0x7c, 0x77, 0x7b, 0xf2, 0x6b, 0x6f, 0xc5, 0x30, 0x01, 0x67, 0x2b, 0xfe, 0xd7, 0xab, 0x76,
0xca, 0x82, 0xc9, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0x59, 0x47, 0xf0, 0xad, 0xd4, 0xa2, 0xaf, 0x9c, 0xa4, 0x72, 0xc0,
0xb7, 0xfd, 0x93, 0x26, 0x36, 0x3f, 0xf7, 0xcc, 0x34, 0xa5, 0xe5, 0xf1, 0x71, 0xd8, 0x31, 0x15,
0x04, 0xc7, 0x23, 0xc3, 0x18, 0x96, 0x05, 0x9a, 0x07, 0x12, 0x80, 0xe2, 0xeb, 0x27, 0xb2, 0x75,
0x09, 0x83, 0x2c, 0x1a, 0x1b, 0x6e, 0x5a, 0xa0, 0x52, 0x3b, 0xd6, 0xb3, 0x29, 0xe3, 0x2f, 0x84,
0x53, 0xd1, 0x00, 0xed, 0x20, 0xfc, 0xb1, 0x5b, 0x6a, 0xcb, 0xbe, 0x39, 0x4a, 0x4c, 0x58, 0xcf,
0xd0, 0xef, 0xaa, 0xfb, 0x43, 0x4d, 0x33, 0x85, 0x45, 0xf9, 0x02, 0x7f, 0x50, 0x3c, 0x9f, 0xa8,
0x51, 0xa3, 0x40, 0x8f, 0x92, 0x9d, 0x38, 0xf5, 0xbc, 0xb6, 0xda, 0x21, 0x10, 0xff, 0xf3, 0xd2,
0xcd, 0x0c, 0x13, 0xec, 0x5f, 0x97, 0x44, 0x17, 0xc4, 0xa7, 0x7e, 0x3d, 0x64, 0x5d, 0x19, 0x73,
0x60, 0x81, 0x4f, 0xdc, 0x22, 0x2a, 0x90, 0x88, 0x46, 0xee, 0xb8, 0x14, 0xde, 0x5e, 0x0b, 0xdb,
0xe0, 0x32, 0x3a, 0x0a, 0x49, 0x06, 0x24, 0x5c, 0xc2, 0xd3, 0xac, 0x62, 0x91, 0x95, 0xe4, 0x79,
0xe7, 0xc8, 0x37, 0x6d, 0x8d, 0xd5, 0x4e, 0xa9, 0x6c, 0x56, 0xf4, 0xea, 0x65, 0x7a, 0xae, 0x08,
0xba, 0x78, 0x25, 0x2e, 0x1c, 0xa6, 0xb4, 0xc6, 0xe8, 0xdd, 0x74, 0x1f, 0x4b, 0xbd, 0x8b, 0x8a,
0x70, 0x3e, 0xb5, 0x66, 0x48, 0x03, 0xf6, 0x0e, 0x61, 0x35, 0x57, 0xb9, 0x86, 0xc1, 0x1d, 0x9e,
0xe1, 0xf8, 0x98, 0x11, 0x69, 0xd9, 0x8e, 0x94, 0x9b, 0x1e, 0x87, 0xe9, 0xce, 0x55, 0x28, 0xdf,
0x8c, 0xa1, 0x89, 0x0d, 0xbf, 0xe6, 0x42, 0x68, 0x41, 0x99, 0x2d, 0x0f, 0xb0, 0x54, 0xbb, 0x16 };
return sbox[num];
}
// The round constant word array, Rcon[i], contains the values given by
// x to th e power (i-1) being powers of x (x is denoted as {02}) in the field GF(2^8)
// Note that i starts at 1, not 0).
int Rcon[255] = {
0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a,
0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63, 0xc6, 0x97, 0x35, 0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef, 0xc5, 0x91, 0x39,
0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd, 0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f, 0x25, 0x4a, 0x94, 0x33, 0x66, 0xcc, 0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a,
0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb, 0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8,
0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a, 0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63, 0xc6, 0x97, 0x35, 0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef,
0xc5, 0x91, 0x39, 0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd, 0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f, 0x25, 0x4a, 0x94, 0x33, 0x66, 0xcc,
0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a, 0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb, 0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b,
0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a, 0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63, 0xc6, 0x97, 0x35, 0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3,
0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef, 0xc5, 0x91, 0x39, 0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd, 0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f, 0x25, 0x4a, 0x94,
0x33, 0x66, 0xcc, 0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a, 0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb, 0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20,
0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a, 0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63, 0xc6, 0x97, 0x35,
0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef, 0xc5, 0x91, 0x39, 0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd, 0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f,
0x25, 0x4a, 0x94, 0x33, 0x66, 0xcc, 0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a, 0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb, 0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04,
0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x4d, 0x9a, 0x2f, 0x5e, 0xbc, 0x63,
0xc6, 0x97, 0x35, 0x6a, 0xd4, 0xb3, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0xef, 0xc5, 0x91, 0x39, 0x72, 0xe4, 0xd3, 0xbd,
0x61, 0xc2, 0x9f, 0x25, 0x4a, 0x94, 0x33, 0x66, 0xcc, 0x83, 0x1d, 0x3a, 0x74, 0xe8, 0xcb };
// This function produces Nb(Nr+1) round keys. The round keys are used in each round to decrypt the states.
void KeyExpansion()
{
int i,j;
unsigned char temp[4],k;
// The first round key is the key itself.
for(i=0;i<Nk;i++)
{
RoundKey[i*4]=Key[i*4];
RoundKey[i*4+1]=Key[i*4+1];
RoundKey[i*4+2]=Key[i*4+2];
RoundKey[i*4+3]=Key[i*4+3];
}
// All other round keys are found from the previous round keys.
while (i < (Nb * (Nr+1)))
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
temp[j]=RoundKey[(i-1) * 4 + j];
}
if (i % Nk == 0)
{
// This function rotates the 4 bytes in a word to the left once.
// [a0,a1,a2,a3] becomes [a1,a2,a3,a0]
// Function RotWord()
{
k = temp[0];
temp[0] = temp[1];
temp[1] = temp[2];
temp[2] = temp[3];
temp[3] = k;
}
// SubWord() is a function that takes a four-byte input word and
// applies the S-box to each of the four bytes to produce an output word.
// Function Subword()
{
temp[0]=getSBoxValue(temp[0]);
temp[1]=getSBoxValue(temp[1]);
temp[2]=getSBoxValue(temp[2]);
temp[3]=getSBoxValue(temp[3]);
}
temp[0] = temp[0] ^ Rcon[i/Nk];
}
else if (Nk > 6 && i % Nk == 4)
{
// Function Subword()
{
temp[0]=getSBoxValue(temp[0]);
temp[1]=getSBoxValue(temp[1]);
temp[2]=getSBoxValue(temp[2]);
temp[3]=getSBoxValue(temp[3]);
}
}
RoundKey[i*4+0] = RoundKey[(i-Nk)*4+0] ^ temp[0];
RoundKey[i*4+1] = RoundKey[(i-Nk)*4+1] ^ temp[1];
RoundKey[i*4+2] = RoundKey[(i-Nk)*4+2] ^ temp[2];
RoundKey[i*4+3] = RoundKey[(i-Nk)*4+3] ^ temp[3];
i++;
}
}
// This function adds the round key to state.
// The round key is added to the state by an XOR function.
void AddRoundKey(int round)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
state[j][i] ^= RoundKey[round * Nb * 4 + i * Nb + j];
}
}
}
// The SubBytes Function Substitutes the values in the
// state matrix with values in an S-box.
void InvSubBytes()
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
state[i][j] = getSBoxInvert(state[i][j]);
}
}
}
// The ShiftRows() function shifts the rows in the state to the left.
// Each row is shifted with different offset.
// Offset = Row number. So the first row is not shifted.
void InvShiftRows()
{
unsigned char temp;
// Rotate first row 1 columns to right
temp=state[1][3];
state[1][3]=state[1][2];
state[1][2]=state[1][1];
state[1][1]=state[1][0];
state[1][0]=temp;
// Rotate second row 2 columns to right
temp=state[2][0];
state[2][0]=state[2][2];
state[2][2]=temp;
temp=state[2][1];
state[2][1]=state[2][3];
state[2][3]=temp;
// Rotate third row 3 columns to right
temp=state[3][0];
state[3][0]=state[3][1];
state[3][1]=state[3][2];
state[3][2]=state[3][3];
state[3][3]=temp;
}
// xtime is a macro that finds the product of {02} and the argument to xtime modulo {1b}
#define xtime(x) ((x<<1) ^ (((x>>7) & 1) * 0x1b))
// Multiplty is a macro used to multiply numbers in the field GF(2^8)
#define Multiply(x,y) (((y & 1) * x) ^ ((y>>1 & 1) * xtime(x)) ^ ((y>>2 & 1) * xtime(xtime(x))) ^ ((y>>3 & 1) * xtime(xtime(xtime(x)))) ^ ((y>>4 & 1) * xtime(xtime(xtime(xtime(x))))))
// MixColumns function mixes the columns of the state matrix.
// The method used to multiply may be difficult to understand for the inexperienced.
// Please use the references to gain more information.
void InvMixColumns()
{
int i;
unsigned char a,b,c,d;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
a = state[0][i];
b = state[1][i];
c = state[2][i];
d = state[3][i];
state[0][i] = Multiply(a, 0x0e) ^ Multiply(b, 0x0b) ^ Multiply(c, 0x0d) ^ Multiply(d, 0x09);
state[1][i] = Multiply(a, 0x09) ^ Multiply(b, 0x0e) ^ Multiply(c, 0x0b) ^ Multiply(d, 0x0d);
state[2][i] = Multiply(a, 0x0d) ^ Multiply(b, 0x09) ^ Multiply(c, 0x0e) ^ Multiply(d, 0x0b);
state[3][i] = Multiply(a, 0x0b) ^ Multiply(b, 0x0d) ^ Multiply(c, 0x09) ^ Multiply(d, 0x0e);
}
}
// InvCipher is the main function that decrypts the CipherText.
void InvCipher()
{
int i,j,round=0;
//Copy the input CipherText to state array.
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
state[j][i] = in[i*4 + j];
}
}
// Add the First round key to the state before starting the rounds.
AddRoundKey(Nr);
// There will be Nr rounds.
// The first Nr-1 rounds are identical.
// These Nr-1 rounds are executed in the loop below.
for(round=Nr-1;round>0;round–)
{
InvShiftRows();
InvSubBytes();
AddRoundKey(round);
InvMixColumns();
}
// The last round is given below.
// The MixColumns function is not here in the last round.
InvShiftRows();
InvSubBytes();
AddRoundKey(0);
// The decryption process is over.
// Copy the state array to output array.
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
out[i*4+j]=state[j][i];
}
}
}
void main()
{
int i;
// Recieve the length of key here.
while(Nr!=128 && Nr!=192 && Nr!=256)
{
printf(“Enter the length of Key(128, 192 or 256 only): “);
scanf(“%d”,&Nr);
}
// Calculate Nk and Nr from the recieved value.
Nk = Nr / 32;
Nr = Nk + 6;
// Part 1 is for demonstrative purpose. The key and plaintext are given in the program itself.
// Part 1: ********************************************************
// The array temp stores the key.
// The array temp2 stores the plaintext.
unsigned char temp[32] = {0x00 ,0x01 ,0x02 ,0x03 ,0x04 ,0x05 ,0x06 ,0x07 ,0x08 ,0x09 ,0x0a ,0x0b ,0x0c ,0x0d ,0x0e ,0x0f};
unsigned char temp2[16]= {0x69 ,0xc4 ,0xe0 ,0xd8 ,0x6a ,0x7b ,0x04 ,0x30 ,0xd8 ,0xcd ,0xb7 ,0x80 ,0x70 ,0xb4 ,0xc5 ,0x5a};
// Copy the Key and CipherText
for(i=0;i<Nk*4;i++)
{
Key[i]=temp[i];
in[i]=temp2[i];
}
// *********************************************************
// Uncomment Part 2 if you need to read Key and CipherText from the keyboard.
// Part 2: ********************************************************
/*
//Clear the input buffer
flushall();
//Recieve the Key from the user
printf(“Enter the Key in hexadecimal: “);
for(i=0;i<Nk*4;i++)
{
scanf(“%x”,&Key[i]);
}
printf(“Enter the CipherText in hexadecimal: “);
for(i=0;i<Nb*4;i++)
{
scanf(“%x”,&in[i]);
}
*/
// ********************************************************
//The Key-Expansion routine must be called before the decryption routine.
KeyExpansion();
// The next function call decrypts the CipherText with the Key using AES algorithm.
InvCipher();
// Output the decrypted text.
printf(“nText after decryption:n”);
for(i=0;i<Nb*4;i++)
{
printf(“%02x “,out[i]);
}
printf(“nn”);
}

